Monday, December 3, 2012
New Region of Space Discovered
NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft has encountered a previously unknown region of space at the edge of the heliosphere described as a "magnetic highway," an area where the Sun's magnetic field lines are connected to interstellar magnetic field lines allowing for greater traffic of lower-charged particles in both directions.
Saturday, December 1, 2012
Ice Found on Mercury
NASA's Messenger spacecraft has discovered evidence of abundant surface water ice on Mercury located in its permanently shadowed polar regions.
Thursday, November 29, 2012
Giant Black Hole Discovered

Wednesday, November 28, 2012
New Type of Matter Created
Collisions of protons and lead ions at the Large Hadron Collider have unexpectedly created a new state of exotic matter called a color-glass condensate, a liquid-like wave of gluons that may result from the phenomenon of quantum entanglement.
Tuesday, November 27, 2012
Comet Belts Discovered
Astronomers have discovered large comet belts surrounding two nearby planetary systems (GJ 581 and 61 Vir) that each contain more than 10 times the comets in our own solar system's Kupier Belt.
Wednesday, November 14, 2012
Rogue Planet Spotted
Astronomers have visually spotted a so-called "rogue planet" (designated CFBDSIR2149-0403), a planet moving through interstellar space and not orbiting a star, just 100 light years distant.
Monday, November 12, 2012
Supersymmetry Result Fails
Results found at Europe's Large Hadron Collider (LHC) show the very rare decay of a Bs meson into two muons, the first time this decay has been observed, providing a failed "golden" test for supersymmetry whose model predicts this decay with much greater frequency than detected.
Saturday, November 10, 2012
New Method of Glass Formation
Scientists have discovered a new way to form glass from a liquid cooling past its melting temperature by the disordered arrangement of nickel-phosphorus polyhedra, the resulting substance classified as a glass by having the mechanical properties of a solid but the amorphous structure of a liquid.
Friday, November 9, 2012
Sensitivity in Alligators, Crocodiles
New research into small pigmented domes called "integumentary sensor organs” (ISO) that line the armored skin of alligators and crocodiles found these are dense spots of mechanoreceptor nerve endings that give the animal an exceptional sense of touch sensitivity greater than human fingertips.
Thursday, November 8, 2012
Tomb of Ancient Egyptian Princess
An unusual tomb of the ancient Egyptian princess Sheretnebty dating to 2500 B.C. was discovered in Abusir South, carved out of bedrock and surrounded by four non-royal high officials, with most of the Fifth Dynasty's royal family buried to the north.
Tuesday, November 6, 2012
World's Rarest Whale Seen
Two spade-toothed beaked whales (Mesoplodon traversii), a mother and calf, stranded themselves and died on a beach in New Zealand, the first time this species known only through partial skulls has been seen and examined as a complete specimen.
Monday, November 5, 2012
Cancer-Resistant Mole Rats
Studies have found both blind mole rats (Spalax spp.) and their cousins naked mole rats (Heterocephalus glaber) have cells that resist tumor growth and make them virtually immune to cancer, the former committing a "concerted cell death" when densities reach a certain level and the latter simply ceasing to grow beyond a certain cell density.
Friday, November 2, 2012
Testing Cope's Rule
Scientists using statistical modeling methods to compare dinosaur femurs have verified Cope's Rule that smaller animals always evolve into larger sizes with no upper limit, with exceptions for structural function between clades such as theropods (two legs) versus sauropods and ornithopods (four legs).
Tuesday, October 30, 2012
Cooking Made Us Human
A new study links the surge in human brain size 1.8 million years ago to the advent of cooking our food, separating Homo erectus from the other primates' inefficient raw diet by unlocking 100% of the digestible nutrition in cooked foods for calorie-expensive brain growth.
Monday, October 29, 2012
Seals as Filter Feeders
Although normally preying on penguins and smaller seals, researchers have found the leopard seal (Hydrurga leptonyx) can feed on tiny krill like a whale by filtering them through specialized teeth, allowing this species to feed from both the top and the bottom of the Antarctic food web.
Wednesday, October 24, 2012
Earth's Magnetic Poles Flipped
Analyzing sediment from the floor of the Black Sea, scientists have determined the Earth's magnetic poles reversed and then reversed again relatively quickly about 41,000 years ago, with the process that normally takes millennia completing its cycle in only about 200 years and during which the magnetic field strength was only one-twentieth what it is today.
Monday, October 22, 2012
Acoustic Analysis of Bridges
Using a technique known as impact-echo testing, engineers have developed a new method to analyze and evaluate the structural stability of a bridge deck based on the acoustic footprint generated by droplets of water striking the surface.
Thursday, October 18, 2012
New Calibration for Carbon Dating
Having two distinct sediment layers that form annually, scientists have used core samples from Lake Suigetsu west of Tokyo to painstakingly account for an atmospheric carbon-14 record stretching back 52,000 years, extending calibration references for a new, more accurate standard for radiocarbon dating.
Wednesday, October 17, 2012
Closest Earth-Sized Planet
Astronomers have confirmed the discovery of a planet only 1.1 times Earth's mass in orbit around the nearby star Alpha Centauri B just 4.4. light years away, unlikely to be habitable due to its orbit but likely the closest possible planet outside our own solar system.
Tuesday, October 16, 2012
New Type of Cosmic Ray
Astronomers have discovered the first new source of cosmic rays 100 years after their first discovery, the new low-energy type originating not from the explosion of supernovae but from the Arches cluster with the particles accelerated by the shock wave of the young stars moving at around 700,000 km/h.
Wednesday, October 10, 2012
Mouse Eggs From Stem Cells
Researchers have produced lab-made viable egg cells from mouse stem cells, capable of being fertilized and growing individuals to birth, maturity and being successfully reproductive themselves.
Tuesday, October 9, 2012
Wasps Have Mechanical Brains
With neurons more than an order of magnitude smaller and thinner than human neurons, the operation of the brains of the miniature greenhouse whitefly parasite (Encarsia formosa) may rely more upon slight mechanical movements to trigger the chemical release of a signal rather than an electrical action potential.
Monday, October 8, 2012
Spider Attack Caught in Amber
A newly discovered fossilized piece of amber from the Hukawng Valley in Myanmar dated between 97-110 million years old displays a spider attack on a parasitic wasp caught in its web, the first and only evidence of such an interaction between these types of species.
Saturday, October 6, 2012
Biodegradable Electronics
Researchers have developed flexible electronic components composed of conductive magnesium and biocompatible silk that can dissolve in water and inside the human body, enabling the design of medical implants that do not require surgical removal.
Friday, October 5, 2012
Ancient Carbon Resurfacing
A new study reveals a significant amount of carbon stored in lakes and rivers -- often thousands of years old -- is still being released into the atmosphere, challenging current models of long-term carbon storage in aquatic systems and its dynamics in modern climatology.
Thursday, October 4, 2012
Advanced Dinosaur Teeth
Paleontologists and engineers studying the fossilized teeth of duck-billed dinosaurs (hadrosaurids) have found them to be more complex than modern grazers such as cows and horses with an amazing capacity to chew tough and abrasive plant matter.
Wednesday, October 3, 2012
Pain-Killers from Snake Venom
Scientists have isolated pain-killing compounds called mambalgins from the venom of Africa's black mamba snake that are as strong as some opiates used today but without the common dangerous side-effects.
Tuesday, October 2, 2012
Ancient Streambed on Mars
NASA's Curiosity Rover has discovered rounded pebbles and gravel on Mars, evidence of an ancient stream with free-flowing water that once existed on the surface of the planet.
Monday, October 1, 2012
Cold Layer Around Venus
The European Space Agency's Venus Express has discovered an unexpected cold layer in Venus' atmosphere 77 miles above the planet's surface with temperatures reaching −283°F, much colder than anything in Earth's atmosphere and able to form carbon dioxide ice.
Thursday, September 27, 2012
Drought Reveals Warsaw Treasure
A drought affecting Poland's Vistula River, at its lowest level since records began in the 18th century, have revealed 12 tons of 17th-century marble pieces looted from Kazimierz Palace during the Swedish Deluge and sinking to the river bottom with the barge that carried them away some 350 years ago.
Wednesday, September 26, 2012
Tectonic Plate Break-Up
Earthquakes of magnitude 8.6 and 8.2 occurring in the Indian Ocean the same day this past April is the latest evidence of geologic stresses pulling apart the Indo-Australian plate and the possible formation of a new tectonic structure for the region.
Monday, September 24, 2012
Antimicrobial Eye Proteins
Researchers have found small fragments of keratin proteins in the human eye have remarkably strong and versatile antimicrobial properties, possibly providing an easily manufactured and biocompatible line of low-cost therapeutic drugs.
Wednesday, September 19, 2012
Stone Age Dental Filling
Locked away in a museum for 101 years, recent x-ray imaging of a 6500-year-old fossilized jawbone originally found in Slovenia reveals an artificial beeswax filling perfectly filling a cavity on a cracked canine tooth, the oldest known example of Neolithic dentistry.
Tuesday, September 18, 2012
Enormous Roman Bath Mosaic
A "pristine" open-air Roman poolside mosaic of some 1600 square feet has been unearthed in a freshly plowed farmer's field in the city of Antiochia ad Cragum in southern Turkey, likely dating back to the third or fourth century A.D.
Monday, September 17, 2012
Astronomical Unit Fixed
Astronomers have elected to abandon the unreliable historical definition of the astronomical unit (AU), traditionally found through a parallax calculation or one transforming angular measurements with a Gaussian constant, and have unanimously adopted the fixed linear value of exactly 149,597,870,700 meters.
Sunday, September 16, 2012
Van Gogh Varnish Discoloration
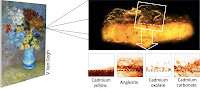
Using sophisticated x-ray beams at two synchrotron sources in Europe, scientists have identified a previously unknown degradation process between paint and protective varnish in Van Gogh's painting, Flowers in a blue vase, a reaction between the cadmium sulphide in the paint and lead ions in the varnish to form an opaque anglesite (PbSO4) and cadmium oxalate (CdC2O4).
Saturday, September 15, 2012
Roman Military Camp Found
The oldest known Roman military fortification in Germany has been found southeast of the city of Trier in the Hunsrueck region, presumably built during Julius Caesar's Gallic War in the late 50s B.C. and providing a rich repository of soldiers' artifacts from this historically significant period.
Friday, September 14, 2012
Atomic Bonds Visualized
Scientists have developed a variant of an imaging method called atomic force microscopy (AFM) to take single-molecule images so detailed that the types of atomic bonds and local distortions in atomic arrangement can be seen.
Monday, September 10, 2012
Ants Have Higher Sense of Smell
Completing the first full map of the olfactory system of ants, researchers have discovered that ants have a dramatically more advanced odor-sensing capability than other species with four to five time more odor receptors than flying insects such as moths, mosquitoes and honeybees.
Thursday, September 6, 2012
Lost Medieval Church Found
Archaeologists have found evidence beneath a parking lot for the Leicester, England, city council offices that is believed to be the lost Greyfriars church, the final resting place of King Richard III, who was buried here in 1485 after his death in the Battle of Bosworth Field.
Wednesday, September 5, 2012
Second of Two Extinction Events
New evidence shows an extinction event occurring 200,000 to 300,000 years before the asteroid impact that wiped out the dinosaurs 65 million years ago, an extended period of huge volcanic eruptions causing extinctions of life on the ocean floor and potentially compromising land-based species prior to the larger event.
Friday, August 31, 2012
Bears Count as Well as Primates
Researchers studying captive black bears at Alabama's Mobile Zoo have found the animals could discriminate between different numbers of grouped items, showing for the first time other animal species can exhibit cognitive counting abilities on a par with primates.
Thursday, August 30, 2012
"Cyborg" Tissue Created
Researchers have grown rat neurons, heart cells and muscle cells on a three-dimensional scaffold of conductive nanowires and silicon sensors, creating viable tissues with embedded electronics that can provide real-time biometrics to monitor the health and activity of these tissues and possibly deliver commands or instructions.
Wednesday, August 29, 2012
Sugar Found in Space
Astronomers have discovered simple sugar molecules (glycoaldehyde) in the gas surrounding a star 400 light years away (IRAS 16293-2422), suggesting such organic components may be more common than expected in the search for interstellar life.
Tuesday, August 28, 2012
New Estimate for Microbial Life
New data from studies of single-celled organisms living in marine sediment on the sea floor at the extremes of nutrient starvation downsize previous estimates by as much as 92%, reducing the overall estimated population of microbial life and biomass on Earth by about half.
Monday, August 27, 2012
EPB Virtually Impassable
First hypothesized by Charles Darwin in 1880, a comprehensive study focusing on robust coral species has confirmed the deep, 4000-mile uninterrupted stretch of water known as the Eastern Pacific Barrier (EPB) separating the eastern from the central Pacific Ocean is virtually impassable by most marine species, with implications for climate research and species-preservation efforts.
Thursday, August 23, 2012
Two New Owl Species
Researchers have discovered two previously unknown owl species in the Philippines: the Cebu hawk-owl, once thought to be extinct due to deforestation, and the Camiguin hawk-owl, originally suspected to be a subspecies but both confirmed as distinctly new species.
Tuesday, August 21, 2012
Bendable Teeth Discovered
Researchers have found the teeth of the suckermouth catfish (Loricariidae) have a section containing more collagen and significantly less calcium, magnesium and phosphate than the rest of the tooth, permitting the tooth to bend and flex as opposed to being the hardest material in their bodies.
Monday, August 20, 2012
Mini Ion Thrusters
Researchers at MIT have developed small, penny-sized electronic engines covered in 500 microscopic tips that emit tiny beams of ions producing 50 micronewtons of force, enough to propel a shoebox-sized satellite through simple orbital maneuvers.
Sunday, August 19, 2012
New Superhard Form of Carbon
Scientists have created a form of carbon clusters, a hybrid mix of crystalline and amorphous structures starting with carbon-60 "cages," that yields a new superhard material capable of indenting diamond.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)



.jpg)













.jpg)











.jpg)











.jpg)






